Product Creation Key Concepts
Products, Product Suites, and Product Lines
Products are packages of entities, called features and feature bundles, that can be sold by a producer. A feature is a software functionality or set of functionalities. Feature definitions created in the FlexNet Operations Producer Portal correspond to product features defined in the product’s code. Features can be grouped into feature bundles for modular control over how the features are packaged in different products. Typically, a feature bundle consists of features grouped by similarity, complexity level, or other defined criteria (grouping features into a feature bundle is optional).
A product suite is a set of products grouped together for promotional purposes or because the products are functionally complementary (grouping products into a product suite is optional).
Products can be assigned to product lines, which define user access rights to product information. Product lines can also be used to group products for searching and reporting purposes.
Important:Product lines are required for FlexNet Embedded licensing and electronic software delivery; otherwise, they are optional. For more information, refer to the sections Getting Started with FlexNet Embedded Licensing and Getting Started with Electronic Software Delivery.
Entity States
The state of an entity, such as a product or its component features or feature bundles, determines how that entity can be referenced in different stages of its configuration. Allowed state transitions are shown in the figure, and the states are described below it.
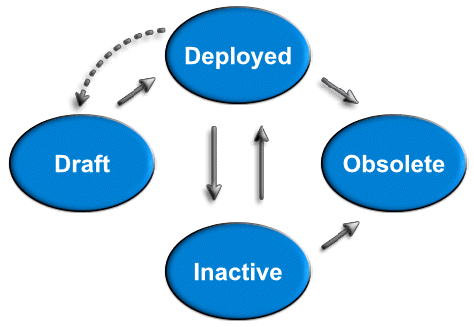
| • | Draft – The default state when an entity is created. In this state, the entity can be edited, but it is not available for production use. |
| • | Deployed – The entity is available for production use. If an entity is deployed accidentally and no other entities refer to it, it can be moved back to draft state. |
| • | Inactive – The entity has been withdrawn from use. No new references can be made to it, but existing references remain unchanged. |
| • | Obsolete – The entity exists only for reporting purposes. While there is existing data that refers to it, no new references can be made. An obsolete entity can be deleted if there are no references to it. |
Changing an entity from one state to another affects the states of related entities. For example, when a product is deployed, its component features and feature bundles are also deployed. However, when a product is made inactive or obsolete, its features and feature bundles are unaffected because a feature or feature bundle can be associated with several different products. A deployed entity may be modifiable, depending on configuration.